Gum abcesses solutions and treatments

Dear readers, welcome to our article on gum abscesses. You’ll find useful information on the treatment of gum abscesses, but please note that our article is no substitute for a consultation with one of our dentists in Geneva! We’ll take the time to answer all your questions! If your questions are not answered in this article, you can get further information in a consultation at the Rhône dental clinic in Geneva!
Gingival abscesses: what you need to know
Gingival abscesses are slightly different from dental abscesses, although they may share some of the same symptoms and treatments. Home remedies can help treat the symptoms, but a dentist will need to treat and drain the abscess.
In this article, learn more about gingival abscesses and how we treat them at the Rhône Dental Clinic in Geneva.
What is a gingival abscess?
The mouth and gums are normally filled with both good and bad bacteria. The accumulation of bad bacteria contributes to the formation of plaque and tartar, which can lead to cavities and other dental problems. If bad bacteria enter an area of open tissue, they can occupy it, multiply and cause infection.Un abcès gingival est une poche infectée du tissu gingival.
A gingival abscess is an infected pocket of gum tissue.
The body reacts by sending white blood cells to fight the infection. To do this, it will induce inflammation in an attempt to block and eliminate the bacteria. The result is a swollen, painful pocket of pus called an abscess. There are two main types of gingival abscess: gingival and periodontal.
- Gingival abscesses occur only in the gum tissue. They have nothing to do with teeth. They can occur if a sharp piece of food lodges directly in the gum and causes an infection.
- Periodontal abscesses occur in the space between the teeth and gums. They are more common in people with periodontal disease, although they can also develop as a result of injury or food stuck between teeth and gums.
Treatment options for gingival abscesses are as follows:
- Dental procedures
- Treatment of a gum abscess includes drainage of the abscess, as well as removal of all contaminants from the area between the gums and teeth. If a person shows signs of plaque buildup or periodontal disease, the dentist may recommend specialized cleaning procedures to help remove accumulated plaque and tartar. The abscess will also need to be drained. The dentist may make a small incision in the inflamed area to drain it. Once the abscess is open and pus is flowing, simply apply pressure to the area to ensure that the pus drains completely.
Dentists often request an X-ray to determine whether the abscess has caused bone degradation. Bone loss can occur in cases of severe infection, or if the gingival abscess is left untreated for a long time. If bone loss is significant, the dentist may recommend procedures to help repair the bone and surrounding tissue. If a gingival abscess affects the inner pulp of the tooth, a root canal will be necessary. In some cases, the dentist may also recommend removing the tooth at the same time as the abscess. People suffering from periapical abscesses, which occur when bacteria invade the dental pulp due to extensive decay, trauma or a cracked tooth, for example, may require root canal treatment or extraction. - Antibiotics
- Antibiotic drugs are another key element in the standard treatment process for gingival abscess. Oral antibiotics can kill the bacteria causing the infection and prevent the infection from spreading or reinfecting the area. They can also reduce inflammation and pain in the area. However, antibiotics do not replace dental care or cure the abscess.
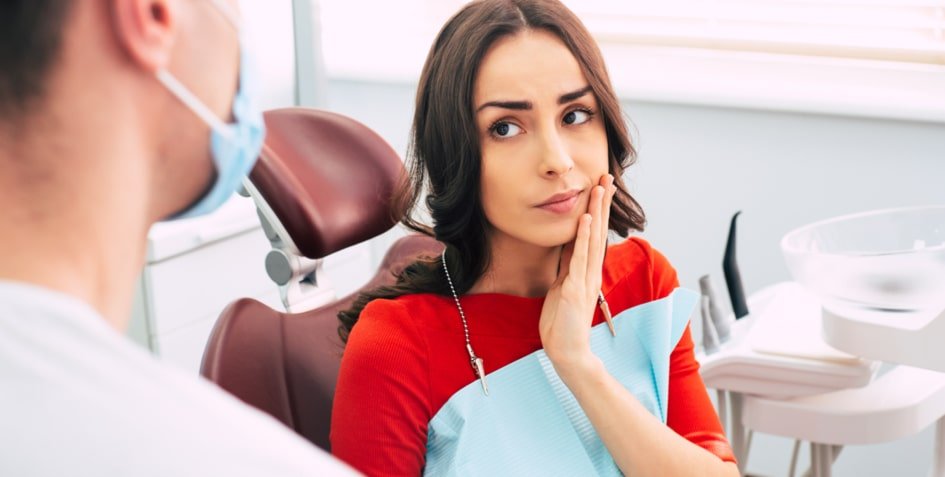
Gum abscess symptoms
The main symptoms of a gum abscess are pain and swelling of the affected area. Depending on the location of the abscess along the gum line, it may also cause pain when chewing or biting. A person may notice a lump or mass in the area of the abscess that causes pain and pressure.
The person may also experience :
- bad breath
- discharge of pus from the mouth
- an unpleasant taste in the mouth
- bleeding gums
- sensitive teeth or gums
- receding gums
- fever
Do you need us to treat a gingival abscess? At your consultation, your particular situation will be discussed in more detail. We encourage you to ask any questions you may have. If any new questions arise after your consultation, please do not hesitate to contact the clinic in Geneva. During the initial examination, we will be able to set up the necessary care for the treatment of gingival abscesses. During this initial examination, we can define the treatment plan, the expected duration of treatment and the approximate cost. Drop into our dental clinic for a visit, or call us on 022 310 50 77 to arrange a consultation.
Article written by Dr. Christophe Gachet of the Rhône Dental Clinic!
– Dr Christophe Gachet
Periodontal abcess is often a patient’s 1st concrete sign of the presence of periodontal disease in the mouth.