Rhône Dental Kids
Your children's dental clinic in Geneva
Take away your child’s fear of the dentist.
Rhône Dental Kids adapts to the most demanding schedules and private requirements of each patient. We guarantee a strict punctuality and offer an emergency service in case of necessity.

Why is it so important to have your child checked by the dentist?
The purpose of a dental check-up is to ensure that your child’s oral development is good and that he or she does not develop cavities, malformations or other disorders that could negatively impact his or her growth. This should be planned from the child’s first birthday in order to establish a follow-up as soon as possible.
What are the risks of waiting too long?
Serious pathologies can set in over time, resulting in pain or infections that have a serious impact on the child’s growth. The problems caused by waiting can be devastating and later turn into heart, respiratory or postural diseases.
Waiting means complications.
In order to avoid health complications for your child, we encourage you to contact your child dentist in Geneva.
1. Why are children afraid of the dentist?
Who hasn’t felt a sense of dread before going to the dentist?
For some, this feeling may be short-lived, while for others it may last for many years.
This apprehension, known as dentophobia (or stomatophobia), affects more than 80% of the population, both children and adults. The trauma can be caused by a bad experience, by fear of pain or simply by an irrational fear.
Although it may seem trivial, in the long term it prevents basic dental care from being carried out and thus promotes dental decay. Sometimes it can lead to a refusal of any dental care. Some people only consult the dentist when they are in severe pain, which sometimes proves to be too late… the dental damage will already be present.
If left untreated, tartar builds up, teeth become increasingly painful, break and fall out.
Dentophobia can thus lead to terrible suffering, both physical and psychological.

2. What is pedodontics?
Pedodontics is a specialty of dentistry dedicated to the care and prevention of children. The practitioner is called a “pedodontist” or “paediatric dentist“.
From the very first contact, they strive to establish a trusting relationship with the child and to provide a positive, non-traumatic experience that will last throughout the child’s life.
For particularly anxious children, our paediatric dentists may offer a conscious sedation method using Meopa (known as ‘laughing gas’). This sedative offers immediate calming power and erases stressful states with no adverse effects, making treatment protocols more effective and comfortable.
This type of sedation is only offered in clinics or hospitals by trained doctors. (See our page dedicated to dentophobia).
The Rhone Dental Clinic protocol limits unnecessary X-rays and exposure to X-rays as much as possible, especially in children. Our hygienists and dentists favour the use of transillumination technology (LED light which allows for a clear view of the teeth) which is safe for health.
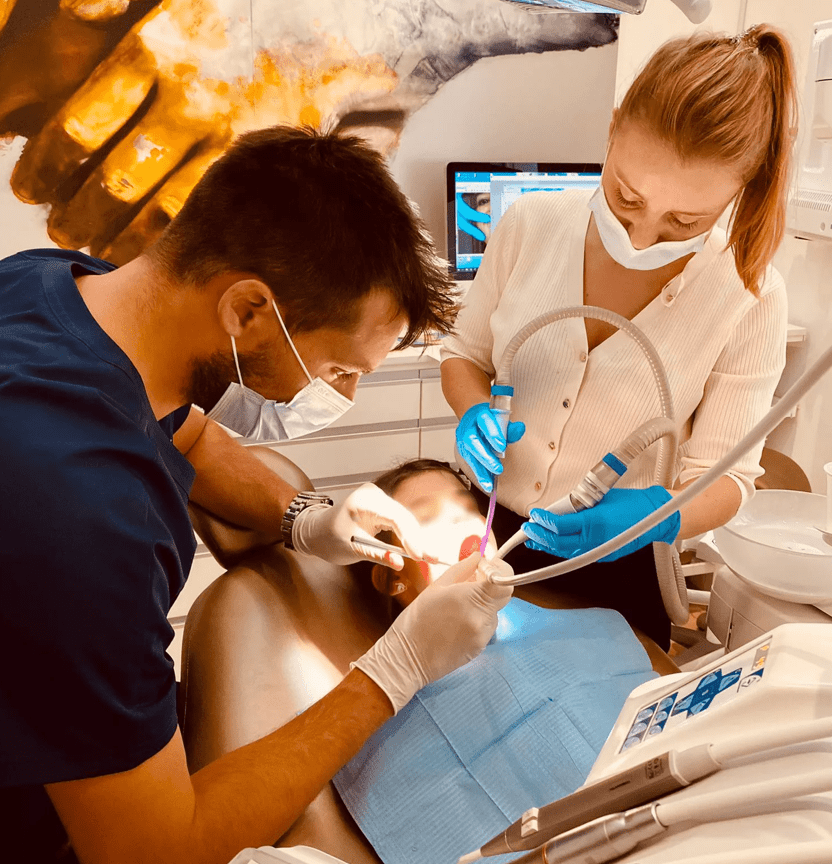
3. What is the first visit to the dentist like?
The role of the first consultation is to meet the child and the parents, to establish an initial relationship of trust.
For this, the child is usually (depending on age) in the chair on the parents’ lap and the consultation begins with a simple discussion between the practitioner, the parents and by involving the child.
This discussion allows us to establish a framework on the caries risk (nutritional assessment, brushing technique and frequency, fluoride…), on the child’s development (symmetry, posture problems, weight) and his current dental condition.
During the 30-minute appointment, the child participates in the consultation in an educational and non-traumatic way.
The exploration of the oral cavity is carried out in the chair with the help of a simple mirror, a probe, and an intraoral camera system that is much appreciated by children and parents (direct visualization).
The younger we can see the patient, the better the future care will be, having been able to assess, anticipate and improve the patient’s cooperation in the chair.
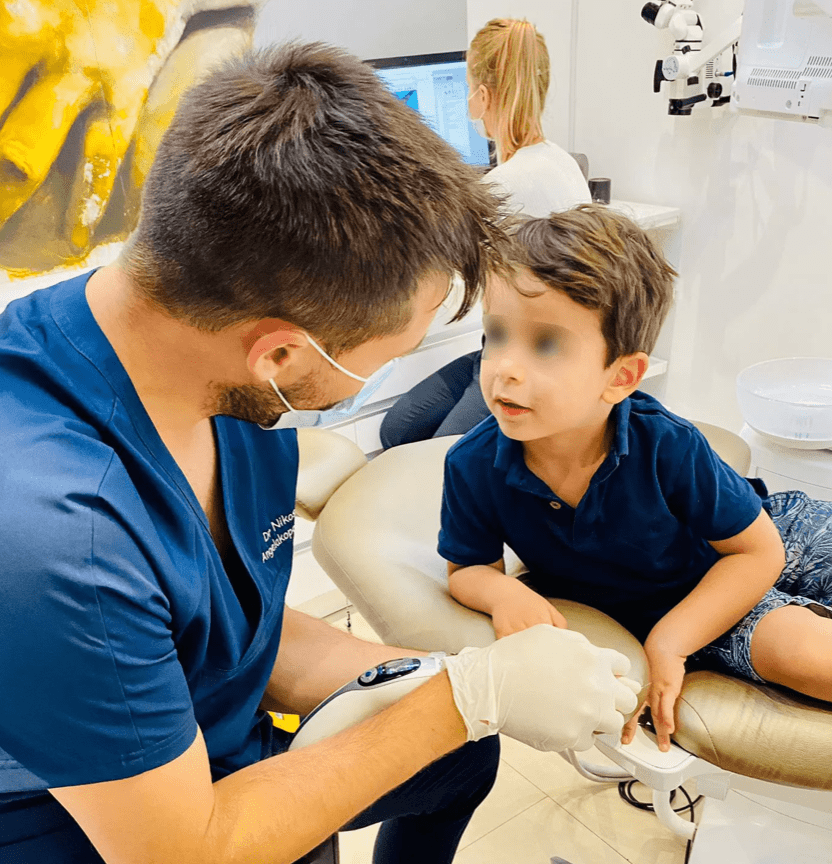

4. What is sedation?
As mentioned above, in certain cases (phobia, history of traumatic experiences, etc.), sedation is necessary in order to carry out treatments in the best possible conditions (for the child and for the quality of the care provided):
The most common sedation is MEOPA: oxygen and nitrous oxide based gas administered by inhalation.
This sedation is a conscious sedation, which means that the child remains awake during the whole of the care, retains its motor capacities (opening the mouth, turning the head, etc.) while being soothed and relaxed (by the euphoric effect of nitrous oxide).
The use of this gas is possible from the age of 4 to 5 years, after an initial consultation with a dental doctor who will make the diagnosis and evaluate with the parents the need or not for this sedation.

5. How to take care of baby teeth?
Parents sometimes tend to neglect them, but the care given to baby teeth determines the condition of the permanent teeth. This is done by brushing the baby teeth every day. According to our dentists, we are now seeing more and more cases of caries from the age of three…
Parents sometimes tend to neglect them, but the care given to baby teeth determines the condition of the permanent teeth. This is done by brushing the baby teeth every day. According to our dentists, we are now seeing more and more cases of caries from the age of three…
From the age of two, you will find suitable toothbrushes and during the first consultation we will explain to your child how to brush his or her teeth properly.
Contrary to popular belief, tooth decay is not only caused by sugar, it is essentially a disease that is transmitted through saliva. It is important to follow the development of your child’s milk teeth. We recommend a gradual introduction of toothpaste for the youngest.
From the first consultation, we will accompany you with the monitoring of your child’s teeth.
Our clinic recommends stopping bottle-feeding or breast-feeding in the evening before bedtime. Milk, whether maternal or artificial, contains a lot of sugar and falling asleep with this liquid in the mouth greatly increases the risk of cavities.

6. What risks do thumbs and dummies pose to teeth?
Sucking is a natural and soothing reflex that a child produces from an early age, even in the womb. Thus, the infant is endowed with a certain sense of sucking which is not only used for feeding. Sucking therefore causes the release of a hormone in the body that is considered a feeling of well-being.
However, advised against by some doctors, the dummy and thumb are still a matter of debate. For or against the thumb and the dummy?
According to specialists, the ideal is to give the dummy only if the child really needs it, and this until the child is about 3 years old. But what are the real consequences for your child’s teeth?
Whether it’s a dummy or a thumb, sucking can disturb the position of the teeth, especially if the child continues to suck after the age of 3. Up to this age, oral deformities can still regress naturally.
Whether it is the dummy or the thumb, sucking can disturb the position of the teeth, especially if the child continues to suck after the age of 3. Up to this age, oral deformities can still regress naturally.
As you can see, in order not to take risks without causing too much frustration, the use of the dummy should be limited over time.

7. How important is nutrition for children's teeth?
When you are at the table with your child, it is very important not to accustom him or her to sugary drinks such as soda or syrups because, in the short, medium and long term, this leads to the destruction of his or her dental enamel and other general disorders.
During the first consultation, a nutritional assessment will be established for the child, with several advices given by Dr Vergnaud.
In absolute terms, it is necessary to avoid daily sugar intake, to avoid nibbling between meals, but to keep the child’s pleasure of consuming sugar by allowing him/her a soda or sweets once a week, without forgetting that he/she must brush his/her teeth well after consumption, which you will check each time.




